It is located in the anterior portion of the abdominal cavity in most vertebrates. Glucose secondary active transport.
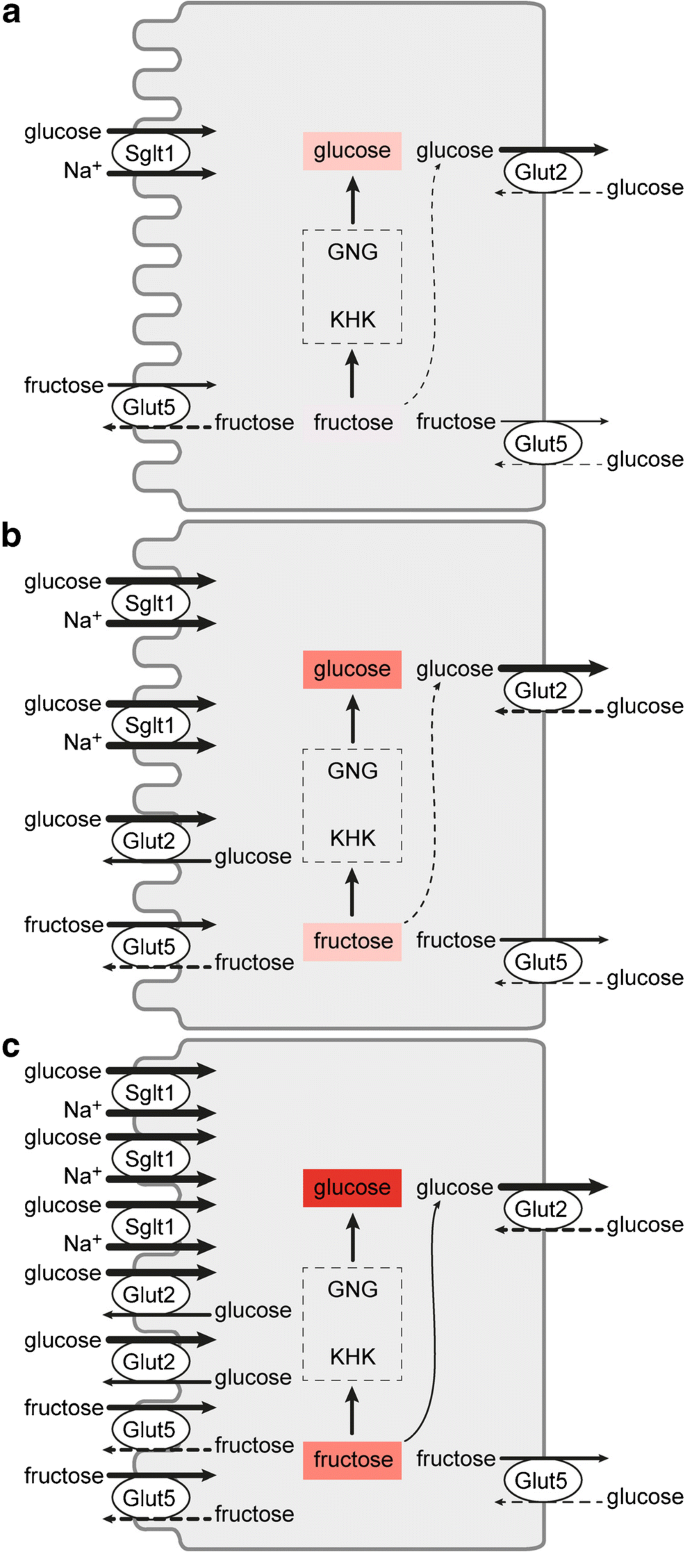
Glucose Transporters In The Small Intestine In Health And Disease Springerlink
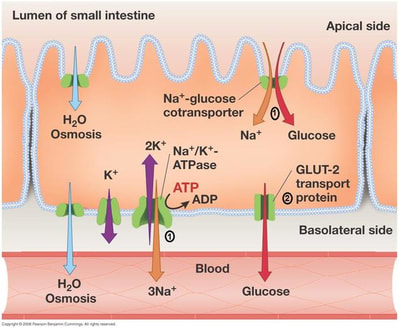
Topic 6 1 Digestion And Absorption Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green

Absorption Bioninja
Glucose generated by digestion of starch or lactose is absorbed in the small intestine only by cotransport with sodium a fact that has exceptionally important implications in medicine.
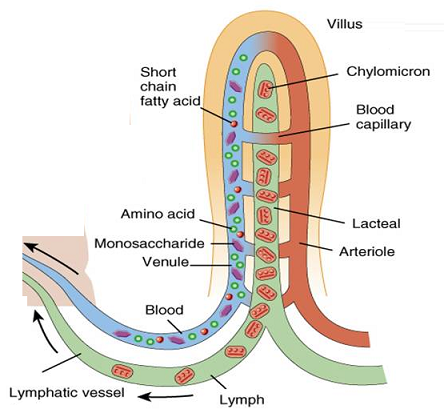
Is glucose absorbed in the small intestine. The small intestine consists of three different parts. It explains what kind of nutrients is absorbed by the blood capillary which is glucose amino acids and can also be nucleotides and by the lacteal which is fatty acids and glycerol. Much of the absorbed glucose circulates to other tissues.
Carbohydrate metabolism begins with digestion in the small intestine where monosaccharides are absorbed into the blood stream. The small intestine or small bowel is an organ in the gastrointestinal tract where most of the absorption of nutrients from food takes place. The three main regions of the small intestine are the duodenum the jejunum and the ileum.
There is no human pathway to metabolise D-lactic acid. These two activities are facilitated by structural adaptations that increase the mucosal surface area by 600-fold including circular folds villi and microvilli. The food is broken down into small components including glucose and is then absorbed through the intestines into the bloodstream.
The use of high-energy waves similar to x-rays to treat a cancer. Its serum concentration is. The stomach serves as a temporary receptacle for the storage and mechanical distribution of food.
The ileum IH-lee-um the final section that leads into the large intestine. In the liver glucose can be converted into glycogen or pyruvate or pentoses for the generation of NADPH for synthetic processes. D-lactic acid is absorbed from the large bowel.
GLUT7 has a high affinity for both glucose and fructose and is located in cells of the small intestine colon testis and. The brain is dependent upon glucose catabolism for its production of ATP. The small intestine contains small finger-like projections of tissue called villi which increase the surface area of the intestine and contain specialized cells that transport substances into the.
There are three sections. α-glucopyranose β-glucopyranose and β-glucopyranose. Ethanol mixes with water and it travels readily through cell membranes.
Difference Between Small Intestine and Large Intestine. Ethanol from alcoholic beverages is absorbed directly through the lining of the digestive tract mostly the stomach and small intestine. The carbohydrate foods we eat are digested into monosaccharides glucose fructose galactose.
It lies between the stomach and large intestine and receives bile and pancreatic juice through the pancreatic duct to aid in digestionThe small intestine is about 18 feet 6 meters long and folds many times to fit in the abdomen. It helps absorb nutrients from food as the food is transported to the large intestine. These enzymes enter the small intestine in response to the hormone cholecystokinin which is produced in response to the presence of nutrients.
Brush Border Hydrolases Generate Monosaccharides. Almost 80 percent of these monosaccharides are glucose. The small intestine is where digestion is completed and virtually all absorption occurs.
GLUT5 is primarily a fructose transporter located on cells of the small intestine testes and kidney where it plays important physiological and pathological roles. The blood then brings these nutrients to the rest of the body. The inner wall of the small intestine is covered with millions of microscopic finger-like projections called villi VIH-lie.
Absorption in the Small Intestine. These monosaccharides are absorbed in the small intestine and transported to the liver through blood. The small intestine is where most chemical digestion takes place.
Glucose either becomes a source of immediate energy or is stored in the liver and muscles in the form of glycogen. Glucose potential energy that is not immediately used is stored by the body as glycogen in the muscles liver and fat. Glucose is usually present in solid form as a monohydrate with a closed pyran ring dextrose hydrate.
Glucose breaks down to form oxygen and carbon dioxide and releases the energy required for various life processes. The duodenum jejunum and ileum. Most of the bodys cells require glucose for energy production.
Insulin glucagon and epinephrine. Pyruvate derived from glucose can be used for lipogenesis. Glucose is absorbed in small intestine by absorptive cells.
The small intestine is the portion of the digestive tract that connects the stomach and the large intestine. Once in the bloodstream the glucose goes through the liver where it either gets turned into glycogen and stored for later use or continues into circulation. The fact that soluble fibre could help improve blood glucose in two ways.
Most of the digestive enzymes in the small intestine are secreted by the pancreas and enter the small intestine via the pancreatic duct. As the human body can only utilize glucose as a source of energy the liver converts fructose and galactose into glucose. From the small intestine it moves across the epithelial cells lining the intestine and then into the blood vessels.
Due to its proximity to the pancreas the duodenum is the section of the small intestine most often affected by pancreatic cancer. Absorption of glucose The transport of nutrients from intestinal lumen into blood stream is called absorption. The picture above is a diagram of what is inside the villus.
The villi are the vehicles through which nutrients can be absorbed into the blood. Blood sugar concentrations are controlled by three hormones. The carbohydrates we eat are broken down into glucose and a few other sugars absorbed by the small intestine and circulated throughout the body.
It raises blood sugar more quickly than other sugars which. In addition the intestine absorbs water and electrolytes thus playing a critical role in maintenance of body water and acid-base balance. Your body is designed to survive and so it stores energy efficiently as fat.
Non-absorbed saccharides pass from the small intestine to the large bowel and they are fermented down to the D-isomer of lactic acid. In aqueous solution on the other hand it is an open-chain to a small extent and is present predominantly as α- or β-pyranose which interconvert see mutarotationFrom aqueous solutions the three known forms can be crystallized. The duodenum the jejunum and the ileum.
Glucose is absorbed directly across the lining of the small intestine into your bloodstream which delivers it to your cells 4 5. Approximately 80 is absorbed by the small intestine 10 by the large intestine and the remaining 10 excreted in the faeces. The slowing down of passage through the digestive gives digestive hormones more time to act and by forming a gel with water soluble fibre prevents carbohydrate from being so quickly absorbed by the small intestine.
The undigested and unabsorbed food passes from the small intestine to the large intestine. Stomach saclike expansion of the digestive system between the esophagus and the small intestine. The brain and nervous system cells rely on glucose for energy and can only function when glucose levels in the blood remain within a certain range.
The blood carries the absorbed food material to different parts of the body. It is a small molecule so it doesnt need further breakdown before it can be absorbed. Virtually all nutrients from the diet are absorbed into blood across the mucosa of the small intestine.

Location Of Monosaccharide Transporters In Enterocytes That Are Download Scientific Diagram

Absorption Function Of The Small Intestine And Significance Of Villi Biology Notes For Igcse 2014

The Apical Glut2 Model Of Intestinal Glucose Absorption Before A Download Scientific Diagram
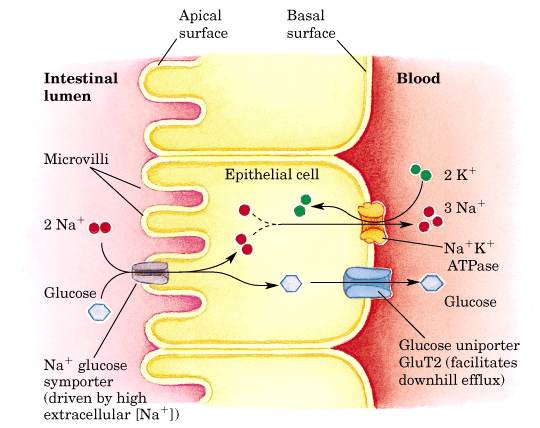
How Is Glucose Absorbed From The Gastrointestinal Tract How Are Blood Glucose Levels Maintained Socratic

Glucose Absorption An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Why Is Glucose Absorbed By Active Transport Not Diffusion Quora
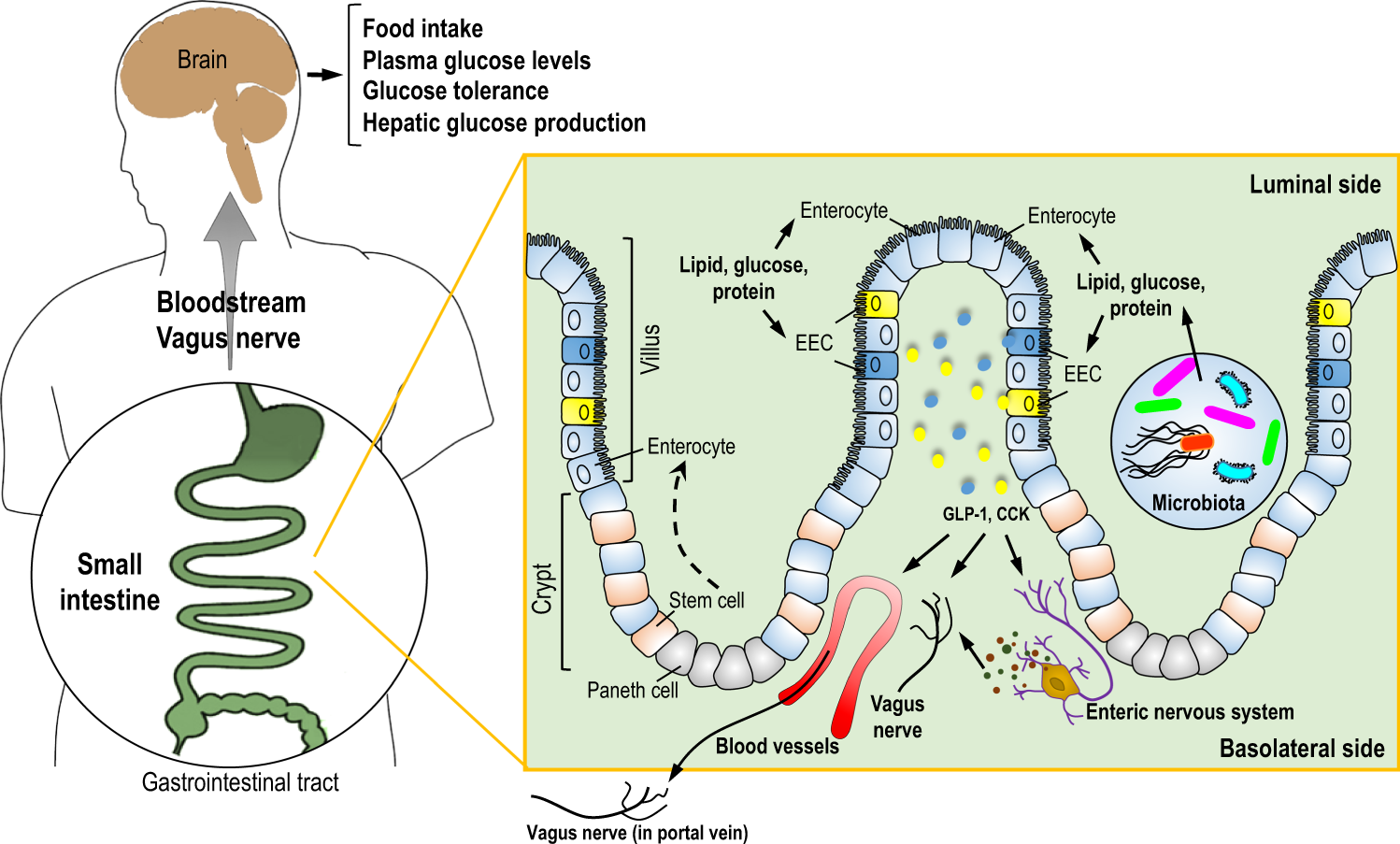
The Metabolic Impact Of Small Intestinal Nutrient Sensing Nature Communications

Carbohydrate Glucose Absorption Youtube

